beta Amyloid
|
|
Conformation-specific beta-Amyloid antibody for Alzheimer's disease research |
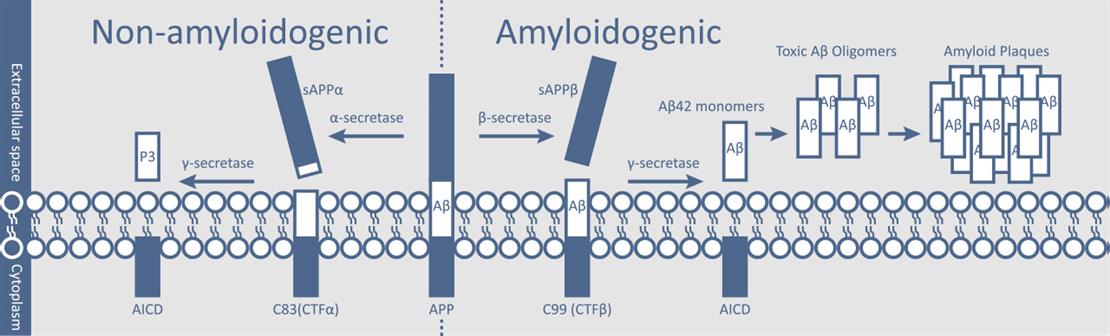
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis is widely believed to be driven by the production and deposition of neurotoxic β-Amyloid peptide (Aβ) aggregates that form plaques in the brain. The Aβ molecules are generated from Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) via β- and γ- secretase cleavage to produce Aβ monomers. Most of the Aβ peptides are 40 amino acids in length (Aβ 1-40, Aβ40), with a small percentage containing 42 residues (Aβ 1-42, Aβ42). These additional two C-terminal amino acids in Aβ42 confer a greater tendency to misfold and subsequently aggregate. Thus, Aβ42 is considered to be more neurotoxic than Aβ40.
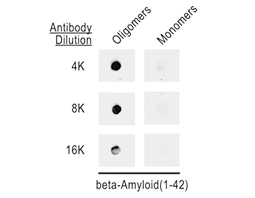
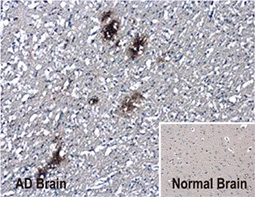
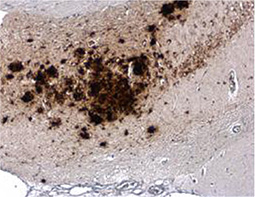
GeneTex’s “beta-Amyloid (1-42) antibody – Conformation-Specific (GTX134510, Rabbit pAb) and (GTX635160, mouse mAb)” against Aβ 1-42 oligomers can specifically detect amyloid plaques in the AD brain by IHC-P analysis. The superior specificity and sensitivity of GTX134510 and GTX635160 were confirmed by dot blot and side-by-side IHC-P comparison.
|
Featured Products |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- Human Aβ (1-42) oligomer immunogen
- Human Aβ (1-42) oligomer immunogen • Validated for dot blot, IHC-P, and ELISA
- High affinity and specificity
- Low background staining
- Detects beta-Amyloid aggregates in human AD brain tissue by IHC-P
- Detects beta-Amyloid aggregates in mouse AD model brain tissue by IHC-P
|
beta-Amyloid (1-42) antibody – Conformation-Specific (GTX134510) |
|
Beta amyloid (1-42) antibody – Conformation Specific antibody [GT622] (GTX635160) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
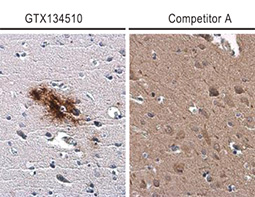
![Beta amyloid (1-42) antibody – Conformation Specific antibody [GT622]_1](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Article/2019/beta-Amyloid/beta-Amyloid_05.jpg)
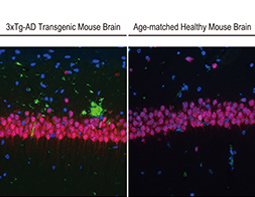
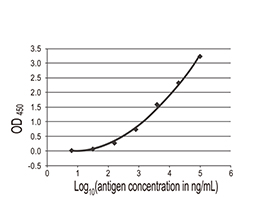
![Beta amyloid (1-42) antibody – Conformation Specific antibody_4[GT622]](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Article/2019/beta-Amyloid/beta-Amyloid_08.jpg)