 |
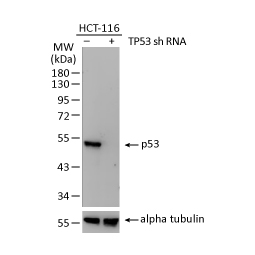
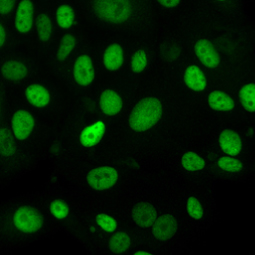
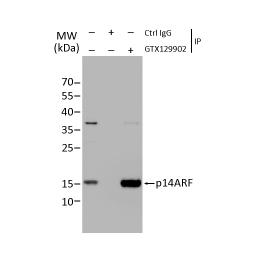
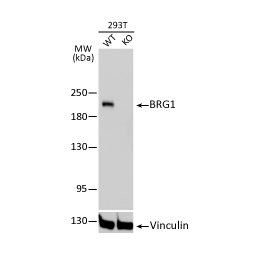
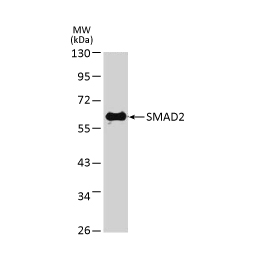
Tumor suppressor gene products, or tumor suppressor proteins, act as barriers to block cells from proceeding down the path to cancer. In contrast to the protein products of proto-oncogenes, some tumor suppressor proteins act to restrain abnormal cell proliferation. Others promote cell death pathways or function in DNA repair. While mutated proto-oncogenes behave in a dominant fashion, tumor suppressor genes are generally recessive, thus requiring that both be inactivated or otherwise compromised in order for cancers to occur. Well-described examples of tumor suppressor proteins include RB, p53, APC and CDKN2A/p14 ARF.
|
Physiological Functions of GPCRs |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||