|
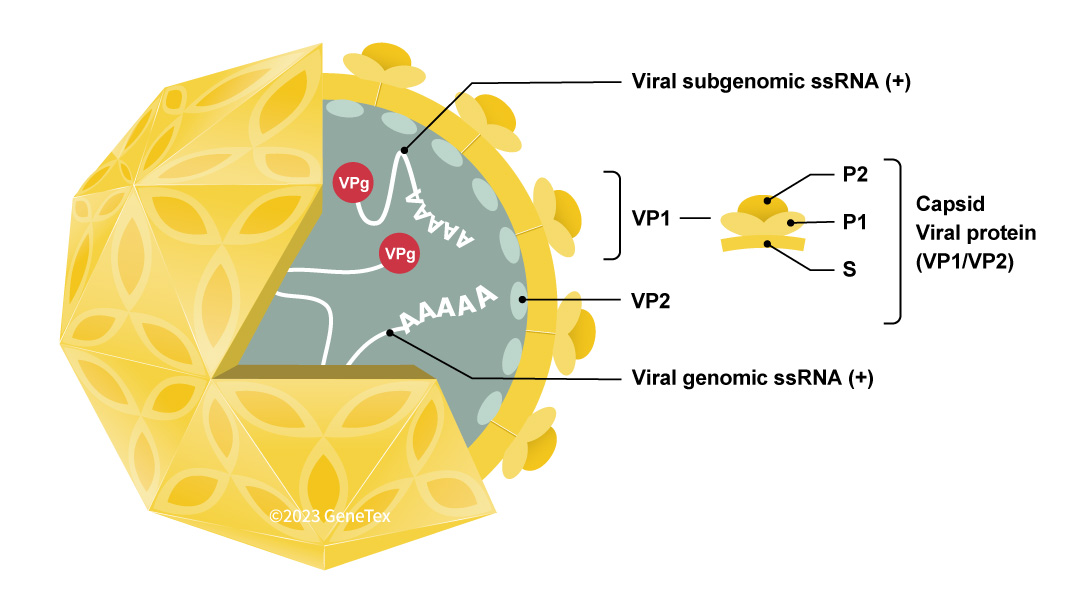
Figure 1. The Norovirus (NoV) virion
|
Human noroviruses (HuNoV) (previously referred to as the Norwalk Virus (NV) or Norwalk-like viruses) are the overwhelming (>95%) cause of epidemic non-bacterial gastroenteritis in the world, accounting for more than 200,000 deaths annually and significant morbidity (1). NoVs spread primarily through the fecal-oral route, which facilitates their spread through children under five years of age, the elderly, the immunocompromised, and tourists. The viral-induced self-limited gastroenteritis generally involves abdominal cramping, watery diarrhea, and vomiting. Though there is at least one vaccine candidate in development, there are no specific antivirals for HuNoVs and thorough handwashing procedures remain the best preventative strategy.
HuNoVs belong to the genus Norovirus of the family Caliciviridae. They are non-enveloped viruses containing a positive-sense, single-stranded genomic RNA of ~7.5-7.7 kb (Figures 1-2). Three open-reading frames (ORFs) encode the six non-structural proteins (NS1/2 to NS7), the main capsid protein VP1, and the minor capsid protein VP2, respectively. There are currently ten genogroups (GI–GX) (further subdivided into 49 genotypes) of NoV specified by the sequences of VP1 and the NS7 polymerase, though only GI (to which NV belongs), GII, and GIV cause acute gastroenteritis in humans (1, 2). The GII.4 genotype is associated with a more severe clinical course, and has spun off six pandemic strains. GII.17 is another highly infectious genotype that has been recently detected. Owing to antigenic shift and drift, new variants with more potent invasive capacity and resistance continue to emerge.
GeneTex is proud to add two new genotype-specific antibodies against HuNoV VP1 to its expanding portfolio of NoV research reagents. These are both recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies: Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] (GTX637271) (GII.4-specific) and Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181) (GII.17-specific). Please see the highlighted product images and a complete NoV antibody listing below.
|

Figure 2. Human NoV genomic organization
|
![Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181)(GII.17-specific)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/Norovirus/landingPage_img_255x255_03.jpg) |
|
Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] GTX638181 (GII.17-specific)
|
|
|
![Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181)(GII.17-specific)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/Norovirus/landingPage_img_255x255_04.jpg) |
|
Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] GTX638181 (GII.17-specific)
|
|
|
![Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] (GTX637271) (GII.4-specific)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/Norovirus/landingPage_img_255x255_01.jpg) |
|
Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] GTX637271 (GII.4-specific)
|
|
|
 |
|
Norovirus VP1 antibody GTX134381 (GII.4-specific)
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
|
Norovirus VP1 antibody GTX134382 (GII.17-specific)
|
|
|
|
| |
|



![Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181)(GII.17-specific)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/Norovirus/landingPage_img_255x255_03.jpg)
![Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181)(GII.17-specific)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/Norovirus/landingPage_img_255x255_04.jpg)
![Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] (GTX637271) (GII.4-specific)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/Norovirus/landingPage_img_255x255_01.jpg)


