|
Figure 1. The EV71 virion |
Discovered in 1969, human enterovirus 71 (EV71) is the causative agent of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) in young children, with a subset of patients developing more severe neurological disease that can result in death. Though epidemics have become more numerous since 1997, there are still no effective therapies or an established vaccine. Clearly, further research into the biology of this virus is of the utmost importance.
As a member of the genus Enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae, EV71 has a positive-stranded RNA genome coding for a 2,194 amino acid polyprotein, which is subsequently processed into four structural (VP1-VP4) and seven non-structural (2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, 3C, 3D) proteins. Identifying the specific functions of these proteins and their interactions with host factors will provide crucial information regarding EV71-associated neural pathogenesis and viral replication.
GeneTex is proud to offer an outstanding selection of antibodies for EV71 research. Please see the highlighted antibodies below or click here to see our latest EV71 research products.
 |
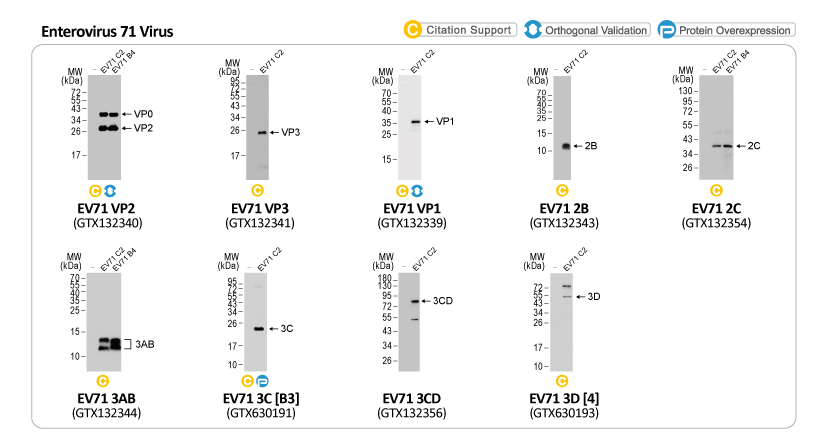
Figure 2. The EV71 genome codes for a single polyprotein that is processed into 11 mature proteins. |
|
Featured Products |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||


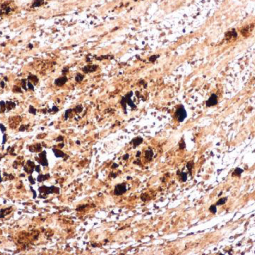
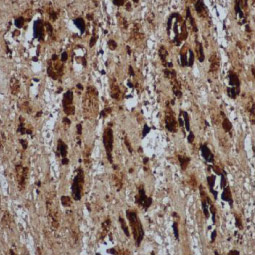
![Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody [HL1928] (GTX637687)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/EV71/landingPage_img_255x255_1.jpg)
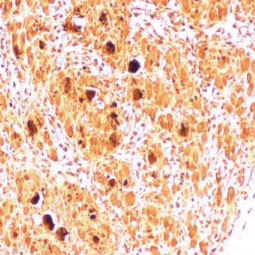
![Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody [HL1929] (GTX637688)](/upload/media/research/Infectious-Diseases/EV71/landingPage_img_255x255_2.jpg)